Reasons and Repercussions of Falling Indian Rupee
The Indian rupee broke a crucial level of 90 - it was at an all-time low of 90.02 against the US dollar on Tuesday (2 December 2025). The rupee has been in a free fall for quite some time now, and multiple factors are driving the fall. In 2025, the rupee has fallen nearly 6% against the US dollar and is among the worst-performing Asian currencies. Let us understand the reasons for the fall and how it will impact everyone in the system.
Reasons for the Falling Indian Rupee
At the beginning of 2025, the Indian rupee traded at ~85 levels per dollar. After falling to 82.2 in May 2025, the Indian rupee has continued to decline, with the 90-level mark breached in December. Here are some of the top reasons for the falling Indian rupee:
Reason 1: Foreign investors are pulling money out
Foreign institutional investors, including hedge funds and large asset managers, have been selling Indian stocks and some bonds this year. When they sell, they convert rupees back into dollars and take the dollars abroad. That adds extra demand for dollars and pushes the rupee down.
Between July 2025 and November 2025, FII have sold Indian equity worth Rs 1.5 lakh crore (approx.)
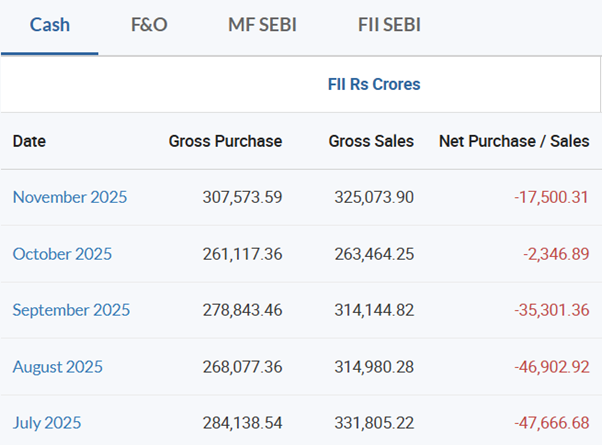
Capital flows are a big source of dollar supply for India. When they stop flowing in or reverse, the market needs dollars elsewhere (importers, hedgers), so the rupee weakens.
Reason 2: Trade deficit widened
India’s trade deficit has widened recently. There has been a big increase in imports such as gold and energy, so more dollars are leaving India to pay foreign sellers. Reports suggest there was a jump in October trade deficit numbers that added pressure. A bigger trade deficit means more sustained demand for dollars from importers. If exports and services receipts don’t keep up, the rupee weakens.
Reason 3: Global dollar strength and rising foreign yields
The US dollar has picked up because of moves in global bond markets and central bank expectations. Higher US Treasury yields (or prospects of higher rates in the US or other major economies) attract capital to dollar assets, making other currencies weaker. Reports point to global yields and expectations (including pressures from other central banks) as amplifying the rupee’s slide. Even if India’s economy is growing fast, money chases the best risk-adjusted returns. If US assets look better (higher yields, safer), capital shifts to dollars and foreign currencies weaken.
Reason 4: Delay in the US trade Deal
Analysts say the rupee is under pressure partly because India and the US have not yet finalised a trade deal to address the high tariffs introduced by US President Donald Trump. Low trade activity and weak portfolio inflows, along with the lack of a US-India agreement, have outweighed the positive effect of India’s strong second-quarter economic growth.
Reason 5: Low domestic inflation
India’s inflation has been relatively low this year. Low inflation, along with nominal depreciation, changes the real effective exchange rate and affects trade competitiveness and valuation metrics. Some analysts point out that the rupee’s nominal fall, combined with low inflation, makes India’s real exchange rate move into undervaluation territory in complex ways. Low inflation reduces pressure for higher interest rates, but it also changes how a currency move is interpreted for competitiveness and real incomes.
Impact of Falling Rupee: Positives & Negatives
Contrary to popular belief, the falling Indian rupee against the USD has both positive and negative sides. Let us start by looking at the positive side of the falling rupee:
Positive 1: Exporters make more money
Most export companies get paid in dollars. When the rupee weakens, every dollar brings in more rupees.
For example, if a software company earns $10 million:
- At Rs 83 per dollar, that is Rs 830 crore
- At Rs 90 per dollar, that is Rs 900 crore
Nothing changed in their business, but their rupee earnings increased. This helps sectors such as IT, pharma, textiles, auto components, and chemicals. Higher rupee revenue improves profits, margins and sometimes even stock prices.
Positive 2: India becomes more attractive for global buyers
A weaker rupee makes Indian goods cheaper compared to competitors.
Think of a European buyer comparing two suppliers, one in India and one in Vietnam. If the rupee becomes cheaper, the Indian product might suddenly look like a better deal. This can help India win more orders in:
- Garments
- Engineering goods
- Specialty chemicals
- Handicrafts
- Leather products
It does not happen overnight, but over months, global buyers shift orders to countries where costs fall.
Now, let us look at the negative impact:
Negative 1: Imports get expensive, and that hits everyone
India imports oil, gas, electronics, machinery, chemicals, basically anything high-tech. When the rupee weakens, the cost jumps even if global prices stay the same. Fuel is the biggest problem because higher fuel prices ripple into:
- Transportation
- Food delivery
- Logistics
- Air travel
- Manufacturing cost
This increases the cost of living for everyone.
Negative 2: Inflation risk goes up
Because imports are expensive, companies slowly raise prices. You feel it a few weeks or months later. Items most affected are:
- Cooking oils
- Gadgets
- Medicines made from imported ingredients
- Cars and electronics
- Packaged food where the packaging material is imported
- It’s not immediate hyperinflation, but steady, annoying price creep that hits household budgets.
Negative 3: Foreign loans become a burden
When a company borrows in dollars, it has to repay that loan in dollars, too. As long as the rupee stays stable, this isn’t a problem. But when the rupee weakens, the company suddenly needs more rupees to buy the same amount of dollars for repayment. So, a loan that looked cheap on paper becomes more expensive in reality. As interest costs rise, the total debt load increases, and profit margins shrink. If the company hasn’t hedged its currency risk, the pressure can be severe.
Airlines, power companies and infrastructure firms often feel this the most because they depend heavily on imported equipment or fuel and already operate with tight margins. This extra burden can strain their cash flow and make their balance sheets look weaker.
Outlook of the Indian Rupee Against the USD
As per Goldman Sachs, recent INR weakness is overstated, and the rupee will likely trade in a range rather than fall steadily. Other banks are mixed: Nomura has been more optimistic, forecasting a stronger rupee by year-end, while DBS expects the currency to recover below ~88 by end-2025.
The near-term outlook is rangebound, with occasional dips toward 90, defended by the RBI. Goldman argues India’s macro is strong, high growth and low inflation, so the currency’s slide looks larger than fundamentals justify. That means expect choppy trading, where the RBI steps in when moves get extreme but lets normal day-to-day volatility play out. Reuters reporting shows that the RBI has already intervened to prevent the rupee from breaching the 90 level. Hedge costs have risen, which feeds short-term volatility.
The medium-term outlook is conditional recovery, but not guaranteed. Several factors could push the rupee back toward the mid-80s: improved foreign investor flows, a softer US dollar, and RBI reserve rebuilding. Nomura’s forecasts (made earlier in 2025) assumed softer dollar momentum and inflows and expected the rupee to strengthen to the low- to mid-80s by year-end. DBS similarly projects an end-2025 level below 88, assuming these forces reassert themselves. But if portfolio outflows continue or India’s trade deficit widens further, that recovery could be delayed or reversed.
Conclusion
The rupee’s fall isn’t a simple story of weakness. It’s the result of a tough global dollar cycle, foreign outflows and a wider import bill hitting at the same time. India’s own fundamentals are still solid, which is why many analysts expect the currency to move in a range instead of sliding endlessly. The pressure is real, especially for import-heavy sectors and companies with foreign loans, but it isn’t a crisis.
The RBI is active in the market, exporters are benefiting, and global conditions can turn quickly. For now, the rupee is adjusting to external shocks rather than signalling any collapse in India’s economic health.