India's Fintech Industry
In recent years, one industry that has seen exponential growth in India is fintech. India has emerged as a global fintech hub - fueled by a tech-savvy population, government initiatives, smartphone penetration, and many more reasons. In this article, we will explore India's fintech industry.
Size of India's FinTech Industry
Let us understand the segments of the fintech industry first. The segments of this industry are payments, digital lending, insurance tech, and wealth tech. The total addressable market of the fintech industry will be around $1.5 trillion by 2025. The Revenue and Assets Under Management will be $200 billion and $1 trillion by 2030, respectively. Here are a few more pointers related to different segments:
- India's digital lending market was valued at $270 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow to $350 billion by 2023.
- India is the 2nd largest Insurtech market in Asia-Pacific and is expected to grow by ~15X to reach $88.4 billion by 2030.
- The Payments landscape in India is expected to reach $100 Tn in transaction volume and $50 billion in terms of revenue by 2030.
- The Indian WealthTech market is expected to grow to $237 billion by 2030 on the back of a growing base of retail investors.
As per Ajay Kumar Choudhary, Non-Executive Chairman & Independent Director, National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the Indian fintech industry at present (2024) is estimated to be around $110 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 31% to reach $420 billion by 2029.
Factors that have led to the growth of the Fintech Industry
In the previous section, we have seen that the Indian fintech industry has grown considerably, and the growth is expected to continue. Here we look at the factors that led to this growth:
- Digital India Initiative: The Digital India campaign was launched in 2015 and aimed to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. This initiative laid the foundation for the widespread adoption of digital payments and fintech solutions across the country. By promoting internet connectivity, digital literacy, and government services online, it created an environment conducive to the growth of fintech.
- Demonetization: The 2016 demonetization move, where the government invalidated the 500 and 1,000 rupee notes, significantly accelerated the adoption of digital payments. As cash became hard to get, many (including people in their 40s and 50s) turned to digital wallets and other fintech solutions for their day-to-day transactions, giving a substantial push to the industry.
- UPI and Digital Payments: The Unified Payments Interface (UPI), launched by the NPCI in 2016, revolutionized the digital payments landscape in India. UPI allows users to transfer money instantly across banks using their smartphones without the need for account details. The UPI's simplicity, speed, and security have made it one of the most popular payment systems in India, with billions of transactions being processed monthly.
- Increased Smartphone Penetration: The widespread availability of affordable smartphones and the rollout of 4G services have significantly increased internet access in India. This, in turn, has provided a massive user base for fintech applications, enabling millions of Indians to access financial services at their fingertips.
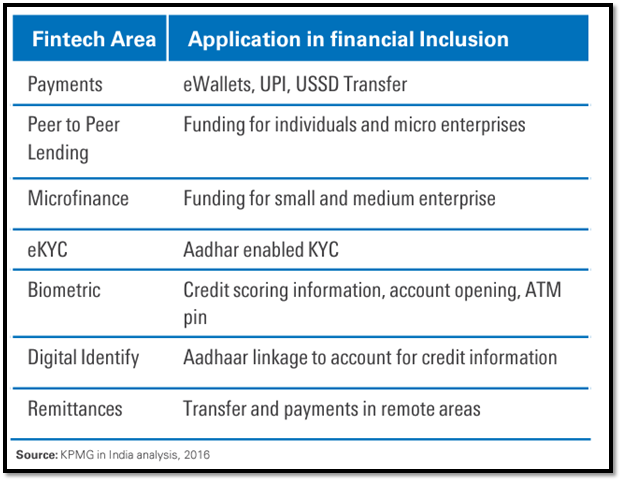
- Regulatory Support: The RBI and other regulatory bodies have played a crucial role in fostering the growth of the fintech sector by creating a conducive regulatory environment. Initiatives like allowing the issuance of payment bank licenses, promoting the use of electronic KYC, and introducing guidelines for peer-to-peer lending and digital lending platforms have been instrumental in the sector's expansion.
Impact of Growing Fintech Industry: Domestic and Global
The exponential growth of the Indian fintech industry is not only having a domestic impact but also globally. Here are some of the impacts.
Domestic Impact
- Financial Inclusion: Fintech has expanded financial services to millions of unbanked and underbanked individuals, promoting financial inclusion.
- Job Creation: The industry has generated numerous employment opportunities, especially in technology and financial services.
- Digital Payments: The rise of digital payments has increased transaction efficiency and reduced the use of cash.
- Improved Financial Literacy: SEBI has spent crores on financial literacy. It won't be wrong to say that fintech companies have also played a role in educating consumers about financial products and services.
- Competition: Fintech's disruptive nature has forced traditional banks to innovate and improve their offerings.
Global Impact
- Innovation Hub: India has emerged as a global fintech hub, attracting investments and talent from around the world. The Indian fintech sector has witnessed funding accounting for a 14% share of Global Funding.
- Technology Export: Indian fintech companies are exporting their solutions to other developing countries.
- Global Partnerships: Collaborations between Indian and foreign fintech players are fostering innovation.
- Soft Power: India's fintech success story enhances its global image as a technological leader.
Way ahead
The Indian fintech industry will continue to expand, and the rural market represents a significant growth opportunity. For the reasons mentioned above, rural areas are likely to see greater adoption of fintech services. We will also see the use of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology is expected to increase in the fintech sector, driving innovations in areas such as fraud detection, credit scoring, and smart contracts.
In recent years, we have seen collaboration between traditional banks and fintech companies, and it is likely to deepen in the coming years, and it will create a more integrated financial ecosystem.
Before you go
India's fintech sector is thriving. With rapid digital transformation across industries, fintech companies are well-positioned for continued growth. Beyond financial inclusion, these innovative firms have a unique opportunity to drive Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) initiatives. This combination of financial success and positive societal impact can fuel sustainable and inclusive economic progress.